Lysergic Acid Diethylamide (LSD) For Sale Online In Portland Oregon
Lysergic Acid Diethylamide, commonly known as LSD or “acid,” is a powerful psychedelic substance that has captivated the curiosity of researchers, psychonauts, and spiritual seekers for decades. First synthesized in 1938 by Swiss chemist Albert Hofmann, LSD became a cultural phenomenon in the 1960s and continues to be a subject of fascination for its profound effects on consciousness, perception, and emotional well-being. This SEO-optimized product description delves into the history, effects, potential benefits, risks, and cultural significance of LSD, providing a comprehensive resource for those seeking to understand this enigmatic compound.
Whether you’re a curious beginner exploring psychedelics for the first time, an experienced user seeking deeper insights, or someone interested in the science and culture surrounding LSD, this guide offers valuable information to support safe and informed decision-making. Let’s embark on a journey to explore the multifaceted world of LSD.
What is LSD?
LSD is a semi-synthetic psychedelic compound derived from ergot, a fungus that grows on rye and other grains. Chemically, it belongs to the ergoline family and is known for its ability to induce altered states of consciousness, vivid hallucinations, and profound psychological experiences. LSD is typically consumed in small doses, often measured in micrograms (μg), due to its extreme potency. A standard dose ranges from 50 to 150 micrograms, with effects lasting 8 to 12 hours or more.
LSD is most commonly ingested orally, often in the form of blotter paper (small squares soaked with the substance), liquid drops, or gelatin squares (“windowpanes”). Its effects are highly dependent on dosage, set (the user’s mindset), and setting (the environment in which it is taken). LSD is not considered physically addictive, and its use is generally associated with psychological rather than physiological dependence.
History of LSD
Discovery and Early Research
LSD was first synthesized by Albert Hofmann in 1938 while working for Sandoz Laboratories in Switzerland. Hofmann was researching ergot derivatives for potential medical applications when he accidentally discovered LSD’s psychoactive properties in 1943 during a self-experiment. This event, famously known as “Bicycle Day” (April 19, 1943), marked the beginning of LSD’s journey into the scientific and cultural spotlight.
In the 1940s and 1950s, LSD was studied extensively for its potential therapeutic applications. Researchers explored its use in treating mental health conditions such as depression, anxiety, and addiction. Early studies suggested that LSD could facilitate profound psychological insights, making it a promising tool for psychotherapy.
The 1960s Counterculture Movement
LSD gained widespread popularity in the 1960s, becoming a symbol of the counterculture movement. Influential figures like Timothy Leary, a Harvard psychologist, advocated for its use as a tool for expanding consciousness and challenging societal norms. The phrase “turn on, tune in, drop out” became synonymous with the psychedelic movement, encouraging individuals to explore altered states of consciousness and reject conventional thinking.
LSD’s association with the counterculture led to its widespread recreational use, particularly among young people. It inspired art, music, and literature, with iconic bands like The Beatles and Grateful Dead incorporating psychedelic themes into their work. However, its growing popularity also led to controversy, as concerns about misuse and safety prompted governments to regulate and eventually criminalize the substance.
Modern Resurgence
In recent years, there has been a renewed interest in LSD and other psychedelics, driven by a growing body of research supporting their therapeutic potential. Organizations like the Multidisciplinary Association for Psychedelic Studies (MAPS) and academic institutions are conducting clinical trials to explore LSD’s efficacy in treating conditions such as depression, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and substance use disorders. This “psychedelic renaissance” has sparked a global conversation about the potential benefits of psychedelics when used responsibly in controlled settings.
How Does LSD Work?
LSD primarily exerts its effects by interacting with serotonin receptors in the brain, particularly the 5-HT2A receptor. Serotonin is a neurotransmitter that regulates mood, perception, and cognition. By binding to these receptors, LSD alters the brain’s neural pathways, leading to changes in perception, thought patterns, and emotional responses.
Neurological Effects
-
Altered Perception: LSD enhances sensory processing, often causing vivid visual and auditory hallucinations. Colors may appear more vibrant, patterns may seem to “breathe,” and sounds may feel more immersive.
-
Synesthesia: Some users experience synesthesia, a phenomenon where senses blend, such as “seeing” music or “hearing” colors.
-
Ego Dissolution: At higher doses, LSD can dissolve the sense of self, leading to feelings of unity with the universe or a loss of personal identity.
-
Time Distortion: Users often report that time feels distorted, with minutes feeling like hours or vice versa.
Psychological Effects
LSD can induce a wide range of psychological experiences, from euphoria and introspection to anxiety and confusion. The nature of the experience depends heavily on the user’s mindset and environment. A positive mindset and a safe, comfortable setting can enhance the likelihood of a meaningful and enjoyable experience, while a negative mindset or chaotic environment may lead to discomfort or a “bad trip.”
Potential Benefits of LSD
While LSD is not approved for medical use in most countries, emerging research and anecdotal reports suggest it may offer several potential benefits when used responsibly under professional guidance. Below are some of the reported benefits:
1. Therapeutic Potential
-
Mental Health Treatment: Preliminary studies indicate that LSD may help alleviate symptoms of depression, anxiety, and PTSD. By facilitating deep emotional processing, LSD can help individuals confront and integrate difficult experiences.
-
Addiction Recovery: Research from the mid-20th century and recent studies suggest that LSD may help individuals overcome substance use disorders, particularly alcoholism, by promoting self-awareness and breaking patterns of addictive behavior.
-
End-of-Life Care: LSD has been explored as a tool for reducing anxiety and improving quality of life in patients with terminal illnesses. It can help individuals come to terms with mortality and find peace.
2. Personal Growth and Creativity
-
Self-Discovery: LSD’s ability to dissolve ego boundaries and foster introspection can lead to profound insights about one’s values, beliefs, and purpose.
-
Creativity Enhancement: Many artists, musicians, and writers have credited LSD with sparking creative breakthroughs. Its ability to alter thought patterns can lead to novel ideas and perspectives.
-
Spiritual Exploration: LSD has been used in spiritual and religious contexts to facilitate mystical experiences and a sense of connection to the universe.
3. Neuroplasticity and Cognitive Benefits
Some researchers believe that LSD may promote neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to form new neural connections. This could have implications for learning, memory, and cognitive flexibility, although more research is needed to confirm these effects.
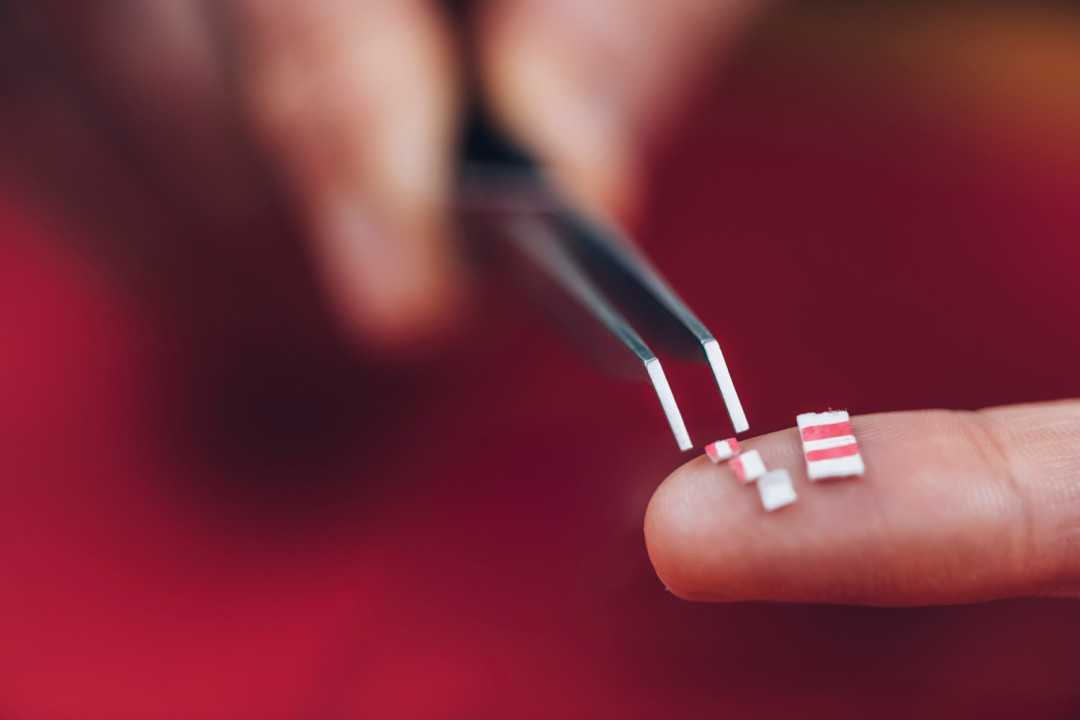

Risks and Safety Considerations
While LSD has a relatively low toxicity profile and is not associated with physical dependence, it is not without risks. Understanding these risks is essential for making informed decisions about its use.
1. Psychological Risks
-
Bad Trips: Negative or overwhelming experiences, known as “bad trips,” can occur, particularly in unprepared individuals or unsuitable environments. These may involve anxiety, paranoia, or confusion.
-
Psychological Vulnerability: Individuals with a history of mental health conditions, such as schizophrenia or bipolar disorder, may be at higher risk of adverse reactions to LSD.
-
Flashbacks: Some users report experiencing “flashbacks” or persistent perceptual changes long after using LSD, a condition known as Hallucinogen Persisting Perception Disorder (HPPD).
2. Legal and Social Risks
LSD is classified as a Schedule I substance in many countries, including the United States, meaning it is illegal to manufacture, possess, or distribute. Legal consequences for LSD use can include fines, imprisonment, or other penalties.
3. Physical Safety
While LSD is not known to cause physical harm in typical doses, its effects can impair judgment and coordination, increasing the risk of accidents or injury. Users should avoid driving, operating machinery, or engaging in other risky activities while under the influence.
Safety Tips for LSD Use
-
Start Low, Go Slow: Begin with a low dose (e.g., 50-100 micrograms) to gauge your sensitivity to the substance.
-
Choose a Safe Setting: Use LSD in a comfortable, familiar environment with trusted individuals present.
-
Have a Trip Sitter: A sober, experienced friend or facilitator can provide support and ensure safety during the experience.
-
Test Your Substance: Use reagent testing kits to verify the purity and authenticity of LSD, as counterfeit substances are common in the illicit market.
-
Avoid Mixing Substances: Combining LSD with alcohol, cannabis, or other drugs can increase the risk of adverse effects.
Cultural Significance of LSD
LSD has left an indelible mark on global culture, influencing art, music, literature, and spirituality. Its impact can be seen in various domains:
1. Art and Music
The psychedelic movement of the 1960s gave rise to a vibrant artistic subculture characterized by bold colors, surreal imagery, and experimental forms. Artists like Andy Warhol and musicians like Jimi Hendrix drew inspiration from the psychedelic experience, creating works that continue to resonate today.
2. Spirituality and Philosophy
LSD has been used as a tool for spiritual exploration across cultures. From indigenous shamanic practices to modern spiritual movements, it has been revered for its ability to facilitate mystical experiences and foster a sense of interconnectedness.
3. Science and Technology
LSD’s influence extends to the tech world, with some Silicon Valley pioneers crediting psychedelics with sparking innovative ideas. For example, Steve Jobs, co-founder of Apple, described his LSD experiences as profoundly influential in shaping his creative vision.
The Future of LSD
As the psychedelic renaissance gains momentum, LSD is poised to play a significant role in both therapeutic and cultural contexts. Ongoing research is exploring its potential in mental health treatment, while advocates are pushing for decriminalization and regulated access. Organizations like MAPS and the Beckley Foundation are at the forefront of this movement, working to destigmatize psychedelics and promote evidence-based policies.
Legalization and Decriminalization
In recent years, several jurisdictions have taken steps to decriminalize psychedelics, including LSD. Cities like Denver, Colorado, and Oakland, California, have passed measures to decriminalize certain psychedelics, signaling a shift in public attitudes. However, widespread legalization remains a complex and contentious issue.
Therapeutic Innovations
Clinical trials are underway to evaluate LSD’s efficacy in treating a range of conditions, from depression to cluster headaches. As research progresses, LSD may become a recognized tool in psychedelic-assisted therapy, offering new hope for individuals with treatment-resistant mental health conditions.
How to Learn More About LSD
For those interested in exploring LSD further, education and community support are key. Here are some ways to deepen your understanding:
-
Read Reputable Sources: Books like The Doors of Perception by Aldous Huxley and LSD: My Problem Child by Albert Hofmann offer valuable insights into the history and effects of LSD.
-
Connect with Communities: Online forums, psychedelic societies, and local meetups provide opportunities to learn from experienced users and advocates.
-
Seek Professional Guidance: If considering LSD for therapeutic purposes, consult with a licensed therapist or facilitator trained in psychedelic-assisted therapy.
-
Stay Informed: Follow organizations like MAPS, the Beckley Foundation, and the Psychedelic Society for updates on research and policy changes.
Conclusion
Lysergic Acid Diethylamide (LSD) is a remarkable substance with a rich history and profound potential. From its discovery in a Swiss laboratory to its role in shaping cultural movements, LSD continues to inspire awe, curiosity, and debate. While its effects can be transformative, they also come with risks that require careful consideration and preparation.
Whether you’re exploring LSD for personal growth, creativity, or therapeutic purposes, approaching it with respect, education, and intention is essential. By staying informed and engaging with supportive communities, you can navigate the psychedelic landscape with confidence and care.
For more information, resources, or personalized support, consider connecting with psychedelic education hubs, consulting with experienced facilitators, or exploring reputable research organizations, Lysergic Acid Diethylamide (LSD) For Sale Online In Portland Oregon. As the world continues to rediscover the potential of psychedelics, LSD remains a powerful tool for unlocking the mysteries of the mind and fostering a deeper connection to ourselves and the universe.





Lily Morgan –
Intense visuals and trips from 2 blotters only i bet the 10 tabs will carry me for the whole week before i will be back for another.